Transpiration teaching resources the science teacher
aqa a-level biology: transpiration Why is transpiration passive and translocation active? Click the card to flip 👆 The energy for transpiration is supplied by the Sun. The energy for translocation is supplied by vascular tissue which carries out active transport, requiring ATP. Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 22 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat
AS Biology Transpiration (OCR A Chapter 9.3) YouTube
¡Precios increíbles y alta calidad aquí en Temu. Envío gratuito en todos los pedidos. No deslizar. Enormes descuentos en nuestros productos aquí - ¡hasta un 90% de descuento!

CohesionTension Theory of Transpiration (A Level Biology) YouTube
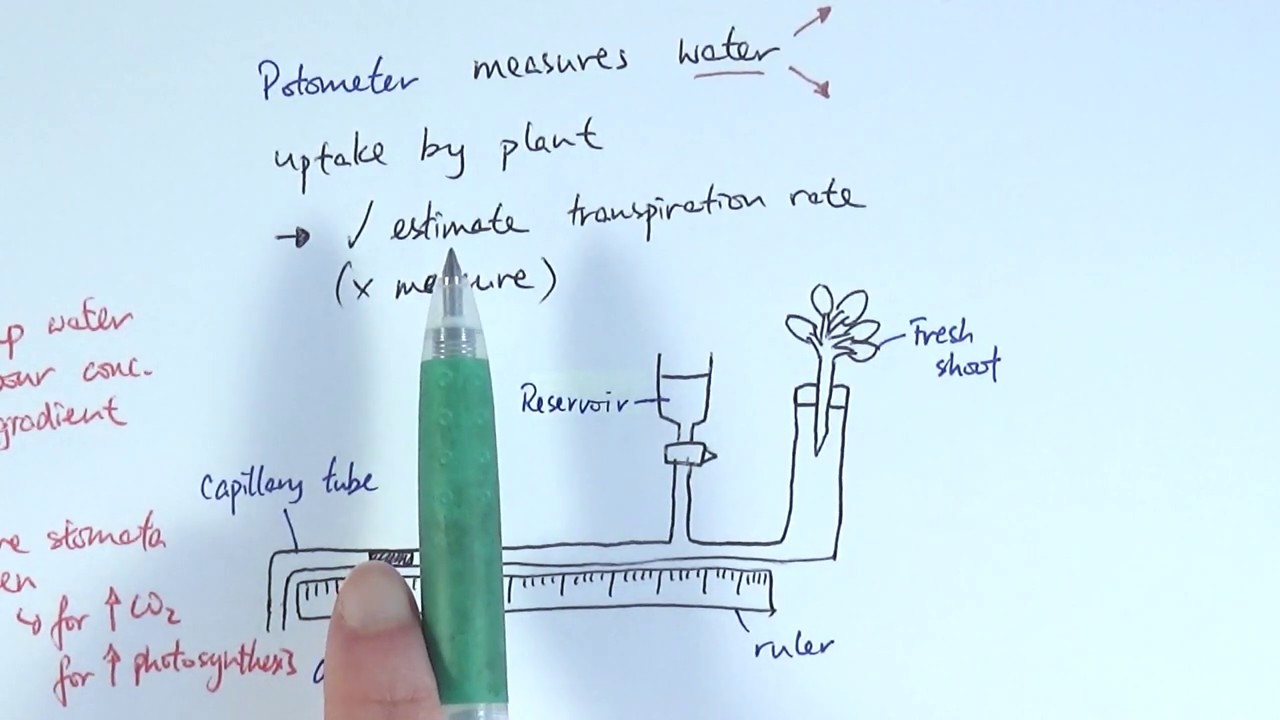
Learn how a potometer shows the rate of transpiration and the associated calculation. Learn how to set up the equipment, collect the data and try some commo.

A Level Biology Transpiration Lesson & Activities Teaching Resources
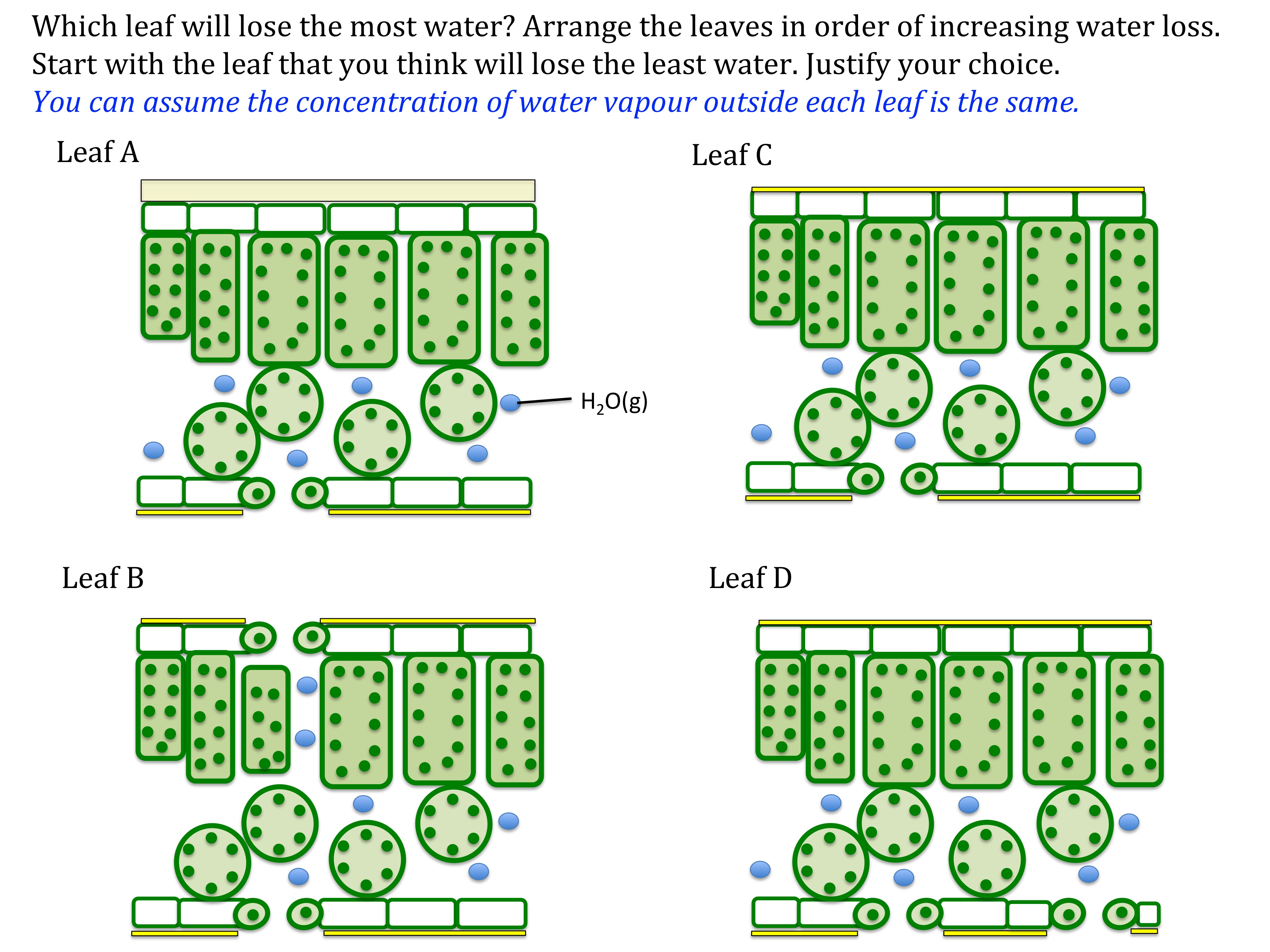
Transpiration involves several cellular structures in the leaf (Figure 4.5.1.2.1 4.5.1.2. 1 ). Water on the surface of mesophyll cells saturates the cellulose microfibrils of the primary cell wall. The leaf contains many large intercellular air spaces for the exchange of oxygen for carbon dioxide, which is required for photosynthesis.

Transpiration and translocation
Freesciencelessons 651K subscribers 5K views 5 months ago A Level Biology "Exchange and Transport in Plants" In this video, we look at transpiration and the cohesion-tension theory of water.

Transpiration in Plants CBSE Class Notes Online Classnotes123
The role of the stomata Transpiration is mainly controlled by the pairs of guard cells that surround stomata (singular stoma) Guard cells open the stomata when they are turgid and close the stomata when they lose water When the stomata are open there is a greater rate of transpiration and of gaseous exchange

OCR A Level Biology (H020) Module 3 Plant transport Transpiration Teaching Resources
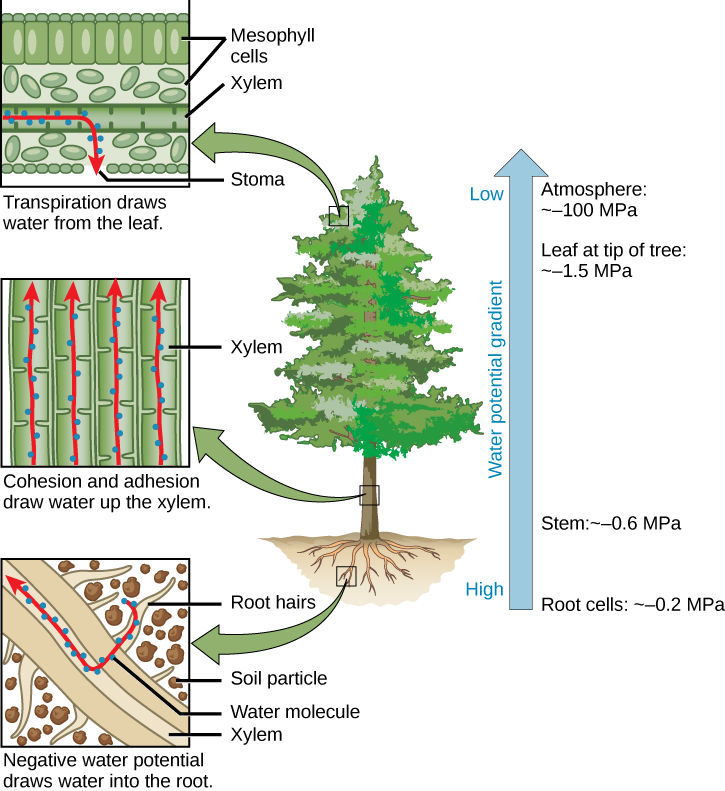
Transpiration is the process in plants by which water travels in a stream from the roots to the leaves where it evaporates. The water is pulled up from the roots through the xylem via the cohesion-tension mechanism. A force called cohesion holds the water molecules together and adhesion holds the water and the cells walls of the xylem together.

Biology & Science Tuition October 2011
This is expressed as ΔΨ. Transpiration is the loss of water from the plant through evaporation at the leaf surface. It is the main driver of water movement in the xylem. Transpiration is caused by the evaporation of water at the leaf-atmosphere interface; it creates negative pressure (tension) equivalent to -2 MPa at the leaf surface.

Download Diagram Showing Transpiration Of Plants for free in 2021 Biology lessons, Biology
Transpiration refers to the loss of water vapour from a plant to its environment by evaporation and diffusion Transpiration is a consequence of gaseous exchange at the stomata The advantage of transpiration is that: It provides a means of cooling the plant via evaporative cooling The transpiration stream is helpful in the uptake of mineral ions

9.3 Transpiration a level biology student
True or false: transpiration is useless to plant function. false. Give four examples of how transpiration is useful to plant functions: it transports useful mineral ions up the plant, maintains cell turgidity, supplies water for growth, cell elongation and photosynthesis, supplies water that evaporates and keeps the plant cool.
11.10 Transpiration Biology LibreTexts
transpiration, in botany, a plant's loss of water, mainly through the stomata of leaves. Stomatal openings are necessary to admit carbon dioxide to the leaf interior and to allow oxygen to escape during photosynthesis. Hence, transpiration is generally considered to be merely an unavoidable phenomenon that accompanies the real functions of.
Transpiration Definition, Factors, Types, and Importance
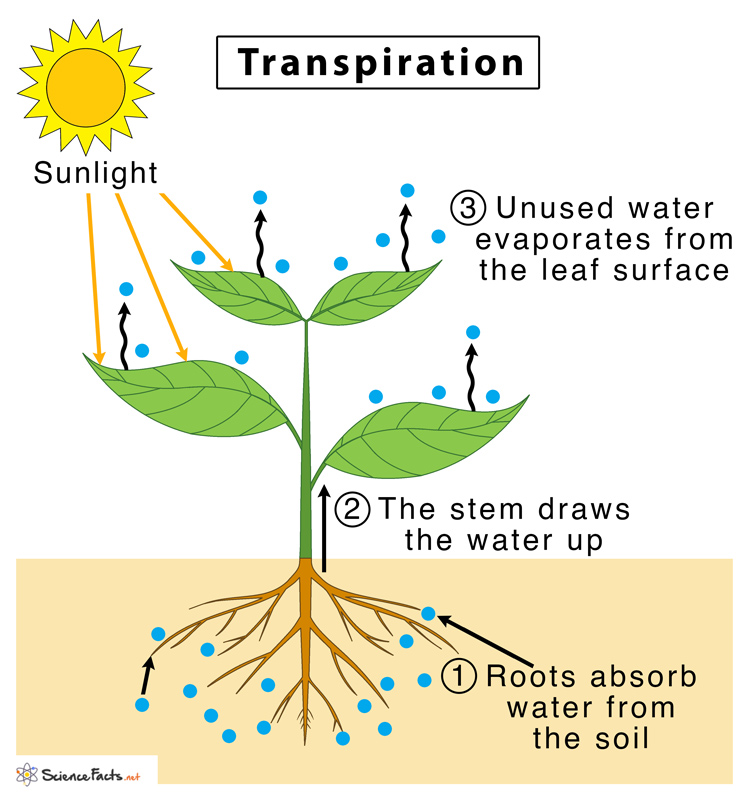
16.2C: Transpiration. Page ID. John W. Kimball. Tufts University & Harvard. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. It occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of CO 2 and O 2 during photosynthesis.

Transpiration Biology Lab Video & Lesson Transcript
How does water move up a plant? We start with the leaf and work backwards to find out.
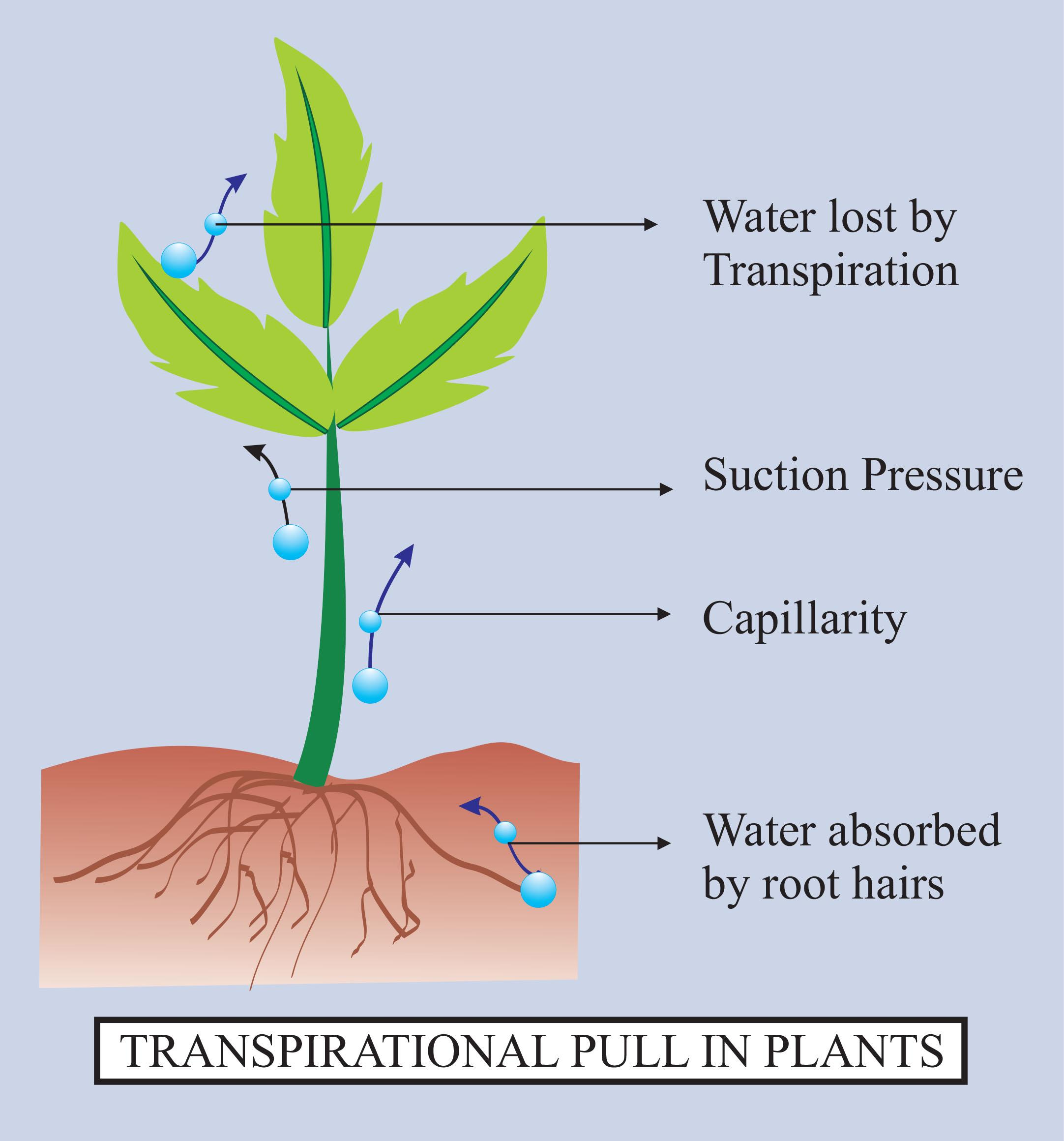
Maximum transpiration takes place from(a)Stem(b)Leaves(c)Roots(d)Flowers and fruits
Transpiration refers to the loss of water vapour via the stomata by diffusion Note that this is different to the transpiration stream which is the movement of water from the roots to the leaves Transpiration is important to the plant in the following ways It provides a means of cooling the plant via evaporative cooling
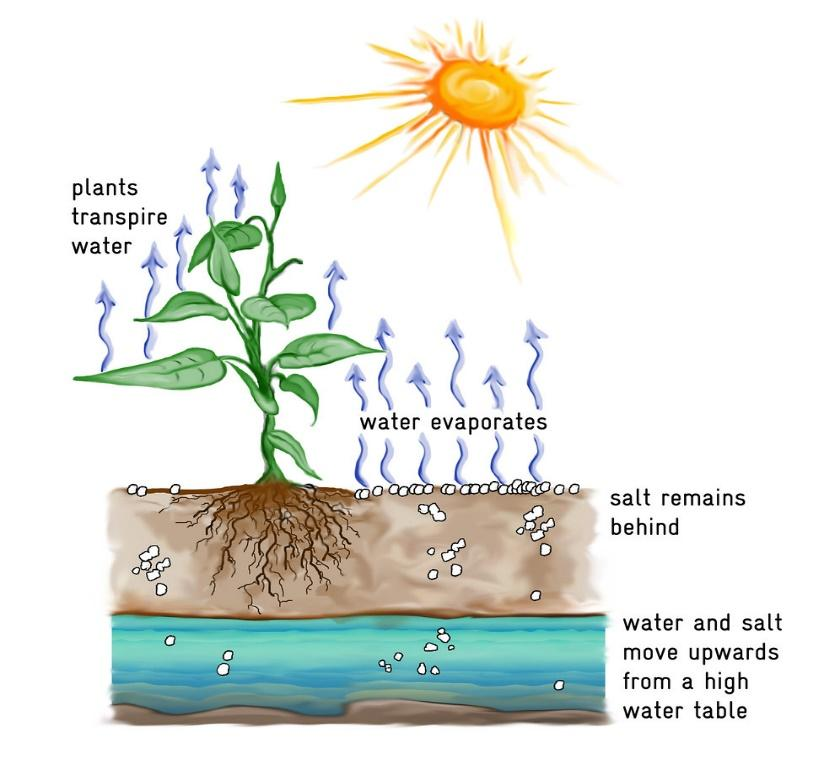
Does transpiration serve any useful function in the plant? Explain.
36.4: Rate of Transpiration. Page ID. John W. Kimball. Tufts University & Harvard. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. It occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of CO 2 and O 2 during photosynthesis.
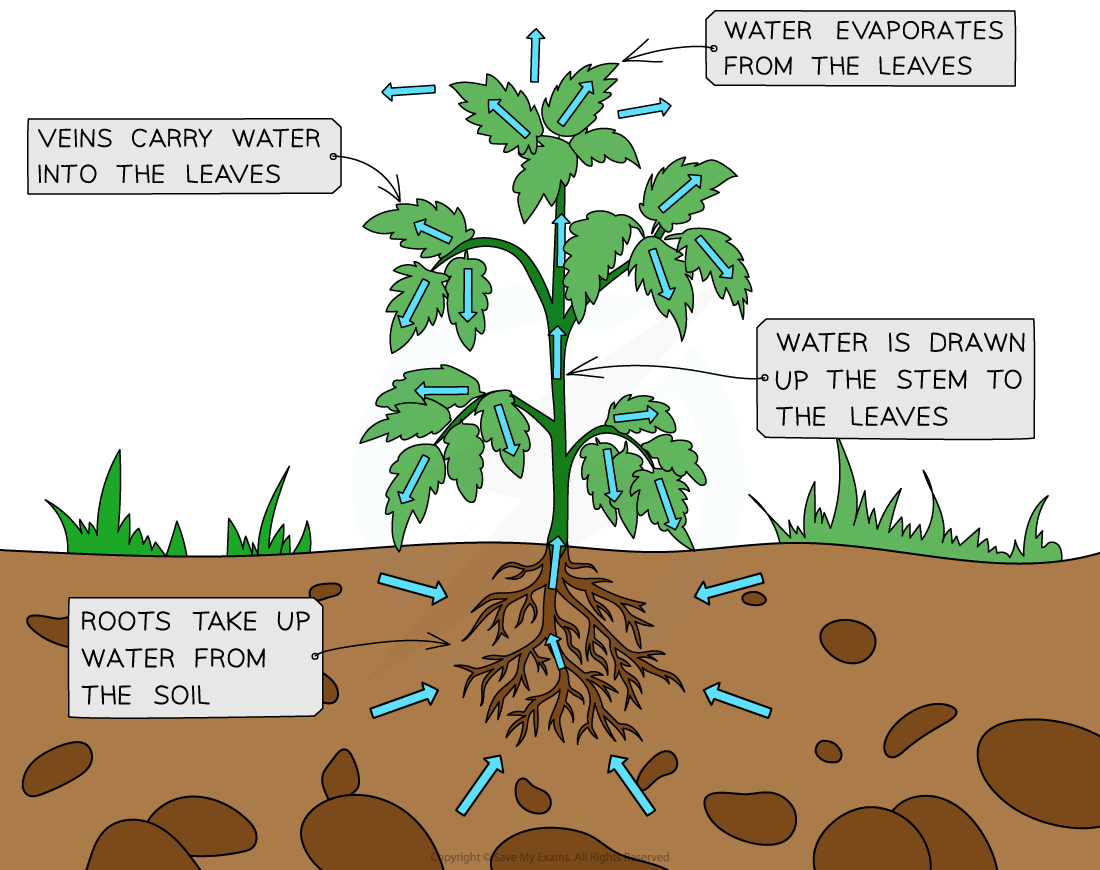
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记3.6.2 Transpiration翰林国际教育
Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. Most of the water absorbed by the roots of a plant—as much as 99.5 percent—is not used for growth or metabolism; it is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. Transpiration is very important for maintaining moisture conditions in the environment.